JOINTS
Joint
is a junction between two or more bones or cartilage.
It
is a device to permit movements.
Classification of Joints:
1. Structural
classification
a. Fibrous
joints
i. Sutures
ii. Syndesmosis
iii. Gomphosis
b. Cartilaginous
joints
i. Primary
cartilaginous joints
ii. Secondary
cartilaginous joints
c. Synovial
joints
i. Ball
and socket
ii. Saddle
iii. Condylar
iv. Ellipsoid
v. Hinge
vi. Pivot
vii. Plane
2. Functional
classification
a.
Synarthroses
(immovable)
b.
Amphiarthroses
(slightly movable)
c.
Diarthroses
(freely movable)
3. Regional
classification
a.
Skull
type (immovable)
b.
Vertebral
type (slightly movable)
c.
Limb
type (freely movable)
4. According
to No. of Articulating Bones
a.
Simple
joint: When only 2 bones are joint.
b.
Compound
joint: When more than 2 bones are joint.
c.
Complex
joint: When joint cavity is divided by an intra articular disc.
Synovial Joints
Synovial
joints are most evolved and so most mobile type of joints.
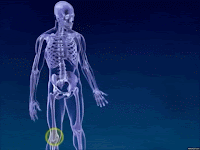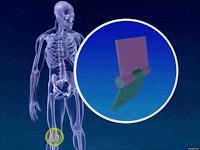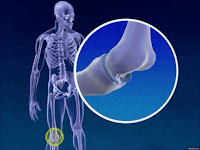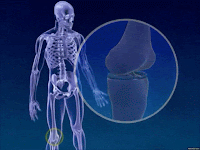
Classification of synovial joint and their movement
1. Plane
or Gliding type: Gliding movement (wrist and ankle)
2. Uniaxial
joints:
a. Hinge
joint: flexion and extension (ankle, elbow)
b. Pivot
joint: Rotation only (head and neck)
3. Biaxial
joints:
a. Condylar
joint: flexion, extension, adjunct rotation/ wrist.
b. Ellipsoid
joint: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction (wrist).
4. Multiaxial
joints:
a. Saddle joint: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and conjunct rotation (joint of thumb).
b. Ball
and socket joint: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction (hip
and shoulder joint).
Mechanical axis of bone: The
mechanical axis of a bone is the straight line connecting the joint centre
points of the proximal and distal joints.
Movement and Mechanism of joints:

1. Angular Movement:
i. Flexion:
Decreasing the angle between bone or 2 parts.
ii. Extension:
Increasing the angle between 2 bones or 2 parts.
iii. Abduction: Moving the part away from the midline.
iv. Adduction:
Bringing the part towards the midline.
2. Rotating Movements:
i. Rotation:
Rotating along the vertical axis.
ii. Circumduction:
Moving the part round in a circle so that the whole part inscribes a cone when
a flexion, abduction, extension and adduction occur in sequence the movement is
called as the circumduction.
3. Gliding:
One part slides on another.
Limitation of Movement:
1.
Reflex
contraction of antagonistic muscles.
2.
Due
to stimulation mechanoreceptors in articular tissue.
3. Ligaments get taut.
4.
Approximation
of soft parts.
Disorders of Joints:
1. Arthritis:
They are of two types
i. Rheumatoid
Arthritis: It is an inflammatory systemic disease resulting in thickened
synovial membranes of small joints of the hands.
- Due
to chronic inflammatory process there is erosion of bones leading to deformity
of the finger.
ii. Osteoarthritis: It is degenerative condition of large weight bearing joints.
- The
articular cartilage wears out, degenerates and there is formation of peripheral
osteophytes.
- The
patients feel lot of pain due to rubbing of bones together during movements of
joints.
2. Spondylitis:
The degenerative change may occur in the cervical spine, leading to narrowed
intervertebral foramen, causing pressure on the spinal nerve.
- This
condition is known as spondylitis.
3.
Neuropathic joints: Neuropathic joint disease (NJD), is a particularly severe form of osteoarthritis.- It
is recognized by severe joint damage in the context of relatively little pain
in the presence of neuropathy and associated with characteristic radiographic
changes in well-established disease.